
Our professional team will support you to go further!
Get a Quote. Ask a Question. We respond within 10 to 15 minutes during business hours.
Softgel capsule manufacturer
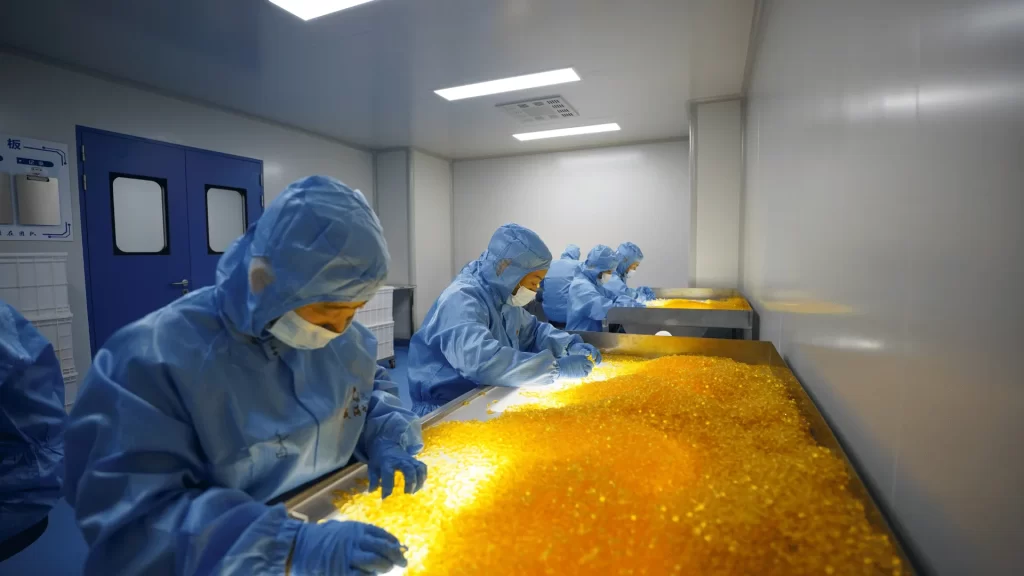

Seeking a Softgel capsule manufacturer that offers high capacity, uncompromising quality, and extensive certifications? Give your brand the competitive edge it deserves. We’re ready to be your dedicated partner, streamlining the manufacturing process to deliver custom, high-quality softgels punctually and cost-effectively.
what is softgel contract manufacturing?

Softgel contract manufacturing is the process where a company outsources the production of softgel capsules—soft, gelatin-based shells filled with liquid or semi-solid ingredients—to a specialized manufacturer. These manufacturers, often called Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) or Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs), handle the entire production process, from formulation to packaging, based on the client’s specifications. Softgels are commonly used for dietary supplements (e.g., fish oil, vitamins), pharmaceuticals, and nutraceuticals due to their ease of swallowing, enhanced bioavailability, and ability to encase sensitive ingredients.
- Formulation Development: The manufacturer works with the client to create a custom liquid or semi-solid fill (e.g., oils, suspensions) and selects shell materials (gelatin or vegetarian alternatives like tapioca starch).
- Gelatin Preparation: Gelatin is melted with water and plasticizers (e.g., glycerin) to form a pliable shell material. Vegetarian softgels may use algae-derived materials.
- Encapsulation: Two gelatin ribbons are formed, and the fill material is injected between them using rotary die machines, creating sealed softgels. This requires precise control of temperature, humidity, and ribbon thickness.
- Drying: Softgels are dried in tunnels or tumblers to remove excess moisture, firming the shell. A stress-relieving step may reduce dimples or bubbles.
- Cleaning and Inspection: Softgels are polished, inspected for defects (e.g., leaks, misshapes), and sorted.
- Packaging: Softgels are bottled, blister-packed, or pouched with custom branding and labeling, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing occurs at every stage—raw materials, in-process, and final product—for potency, purity, and safety, including checks for heavy metals and microbial contamination.
Features of working with Softgel capsule manufacturer:
Working with a softgel capsule manufacturer offers distinct advantages for businesses aiming to produce high-quality dietary supplements, pharmaceuticals, or nutraceuticals. Based on industry practices and the context of contract manufacturing, here are the key features of partnering with a softgel capsule manufacturer:
- Customized Formulations:
- Manufacturers collaborate to develop tailored liquid or semi-solid fills (e.g., oils, suspensions) using ingredients like fish oil, vitamins, or CBD, optimized for bioavailability and client specifications.
- Options for unique blends, potency levels, or specialized actives to differentiate your product.
- Flexible Capsule Design:
- Choice of softgel shell materials, including traditional gelatin or vegetarian/vegan alternatives (e.g., tapioca starch, algae-based).
- Customization of capsule size, shape, color, and transparency to align with brand identity or consumer preferences.
- Private Label and Branding:
- Full private label services allow clients to market softgels under their own brand with custom logos, labels, and packaging (e.g., bottles, blisters, pouches).
- Support for designing consumer-friendly packaging that meets regulatory labeling requirements.
- Advanced Manufacturing Technology:
- Utilization of precision rotary die encapsulation machines to ensure consistent fill accuracy and hermetic sealing, protecting sensitive ingredients from oxidation or degradation.
- Capabilities for specialized softgels, such as chewable, enteric-coated, or time-release formulations.
- Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance:
- Adherence to stringent standards like Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), FDA, Health Canada, or ISO certifications.
- Comprehensive testing for purity, potency, microbial contamination, and heavy metals at every stage, ensuring safe, market-ready products.
- Scalable Production:
- Flexible production runs, from small batches for startups or clinical trials to large-scale commercial orders.
- High-capacity facilities ensure timely delivery, even for high-demand products.
- End-to-End Support:
- Guidance through formulation, regulatory compliance, ingredient sourcing, and market launch, reducing complexity for clients.
- Expertise in navigating global regulatory requirements for different markets.
- Cost Efficiency:
- Outsourcing eliminates the need for clients to invest in expensive equipment, cleanroom facilities, or specialized staff.
- Transparent pricing and economies of scale help keep projects within budget.
- Enhanced Bioavailability:
- Softgels are ideal for lipid-based or poorly soluble ingredients, offering improved absorption compared to tablets or hard capsules.
- Manufacturers can incorporate technologies like nanoemulsions or liposomal delivery for better efficacy.
- Sustainability and Innovation:
- Options for eco-friendly materials, such as plant-based shells or biodegradable packaging, to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Access to trending ingredients (e.g., algae-derived omega-3, plant-based actives) and innovative formats to stay competitive.
- Fast Turnaround and Reliability:
- Streamlined processes and efficient drying, polishing, and packaging ensure quick production timelines.
- Reliable supply chains and delivery schedules meet tight market deadlines.
- Consumer Appeal:
- Softgels are easy to swallow, tasteless, and visually appealing, enhancing consumer satisfaction.
- Options for flavored or odor-masked softgels improve user experience, especially for products like fish oil.
By partnering with a reputable softgel capsule manufacturer, businesses gain access to specialized expertise, cutting-edge technology, and flexible solutions to create high-quality, consumer-friendly products efficiently. If you’d like specific manufacturer recommendations, real-time insights from X posts, or a deeper focus on any feature, let me know!
soft capsule size chart
Here is a table showing common softgel capsule sizes based on shape and approximate fill volume (in CC/mL and Minims). Please note that dimensions can vary slightly between manufacturers, and fill weight depends on the density of your specific formula.

| Shape | Common Size Designation | Approx. Volume (CC / mL) | Approx. Volume (Minims) | Approx. Dimensions (Length x Width in mm)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oval | 3 Oval | 0.15 - 0.19 | 2.4 - 3.0 | ~8.7 x 5.7 |
| 5 Oval | 0.27 - 0.31 | 4.3 - 5.0 | ~10.8 x 6.7 | |
| 7.5 Oval | 0.38 - 0.46 | 6.2 - 7.5 | ~12.6 x 7.6 | |
| 12 Oval | 0.51 - 0.74 | 8.3 - 12.0 | ~15.5 x 9.2 | |
| 16 Oval | 0.76 - 0.99 | 12.4 - 16.0 | ~17.5 x 10.0 | |
| 20 Oval | 1.05 - 1.23 | 17.0 - 20.0 | ~18.8 x 11.1 | |
| Oblong | 4 Oblong | 0.18 - 0.25 | 3.0 - 4.0 | ~10.5 x 5.5 |
| 6 Oblong | 0.31 - 0.37 | 5.0 - 6.0 | ~11.5 x 6.2 | |
| 8 Oblong | 0.40 - 0.49 | 6.5 - 8.0 | ~12.8 x 6.9 | |
| 12 Oblong | 0.68 - 0.79 | 11.0 - 12.0 | ~15.8 x 8.3 | |
| 20 Oblong | 0.99 - 1.23 | 16.0 - 20.0 | ~19.0 x 9.7 | |
| 24 Oblong | 1.23 - 1.48 | 20.0 - 24.0 | ~20.3 x 10.2 | |
| Round | 3 Round | 0.14 - 0.19 | 2.2 - 3.0 | ~7.6 x 7.6 |
| 5 Round | 0.20 - 0.31 | 3.2 - 5.0 | ~8.4 x 8.4 | |
| 9 Round | 0.43 - 0.55 | 7.0 - 9.0 | ~9.9 x 9.9 | |
| 15 Round | 0.74 - 0.93 | 12.0 - 15.0 | ~11.6 x 11.6 | |
| 28 Round | 1.35 - 1.85 | 22.0 - 30.0 | ~14.3 x 14.3 | |
| 40 Round | 1.97 - 2.53 | 32.0 - 41.0 | ~16.2 x 16.2 | |
| Tube | 5 Tube | 0.15 - 0.31 | 2.5 - 5.0 | Varies by length |
| 8 Tube | 0.37 - 0.49 | 6.0 - 8.0 | Varies by length | |
| 17.5 Tube | 0.92 - 1.05 | 15.0 - 17.0 | Varies by length | |
| 30 Tube | 1.66 - 1.97 | 27.0 - 32.0 | Varies by length |
Types of Softgel Capsules
These are the main categories based on shell composition and how the softgel is designed to function after consumption. Softgels also vary by Shape and the specific Fill Material they contain, but these are usually considered characteristics rather than fundamental types.
| Softgel Type | Key Feature(s) | Typical Use / Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Gelatin Softgel | Shell made from animal gelatin, water, and plasticizers (e.g., glycerin). | Traditional type; widely used for oils, liquids, and semi-solids; cost-effective; easy to swallow for many. |
| Vegetarian / Vegan Softgel | Shell made from plant-based materials (e.g., HPMC, Pullulan, modified starch). | Alternative for individuals with dietary, religious, or ethical restrictions regarding animal products. |
| Standard Release Softgel | Shell dissolves in the stomach upon ingestion. | Most common type; provides relatively rapid release of contents in the stomach. |
| Enteric-Coated Softgel | Has a special coating that resists dissolution in the acidic stomach environment. | Protects acid-sensitive ingredients; prevents stomach irritation; reduces aftertaste (e.g., fish oil burps); targets intestinal delivery. |
| Chewable Softgel | Modified shell and fill designed to be chewed; often flavored. | Easier administration for individuals with swallowing difficulties (children, elderly); improved taste experience for unpalatable fills. |
| Twist-Off Softgel | Designed with a tab to be twisted or snipped off to release liquid contents. | Allows for precise dosing of liquids; suitable for pediatric, veterinary, or topical applications. |
How Does softgel contract manufacturing Work?
Softgel contract manufacturing involves outsourcing the production of softgel capsules—soft, gelatin-based shells filled with liquid or semi-solid ingredients—to a specialized manufacturer, often called a Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) or Contract Manufacturing Organization (CMO). These manufacturers handle the entire process, from formulation to finished product, based on the client’s requirements.

- Formulation and Development:
- The manufacturer collaborates with the client to design a custom liquid or semi-solid fill (e.g., fish oil, vitamins, CBD) optimized for bioavailability and stability.
- Shell materials (gelatin or vegetarian alternatives like tapioca starch) are selected, and formulations are tested for compatibility and regulatory compliance.
- Raw Material Sourcing and Testing:
- High-quality ingredients are sourced from vetted suppliers.
- Materials undergo rigorous testing for purity, potency, and contaminants (e.g., heavy metals, microbes) to meet standards like Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
- Gelatin/Shell Preparation:
- Gelatin (or plant-based alternatives) is melted with water and plasticizers (e.g., glycerin) to create a pliable, elastic shell material.
- The mixture is formed into thin, continuous ribbons for encapsulation.
- Encapsulation:
- Using rotary die machines, two gelatin ribbons are molded into capsule shapes while the liquid or semi-solid fill is precisely injected between them.
- The softgels are sealed in one continuous process, ensuring a hermetic seal to protect contents from oxidation or leakage.
- Drying and Curing:
- Freshly formed softgels are dried in controlled tunnels or tumblers to remove moisture, hardening the shell.
- A stress-relieving step may be applied to eliminate imperfections like dimples or bubbles.
- Cleaning and Inspection:
- Softgels are polished to remove residue and visually inspected for defects (e.g., leaks, irregular shapes).
- Automated systems or manual checks ensure uniformity and quality.
- Quality Control:
- Samples are tested for fill accuracy, shell integrity, dissolution, and compliance with regulations (e.g., FDA, Health Canada, ISO).
- Final products are verified for potency, purity, and safety.
- Packaging and Labeling:
- Softgels are bottled, blister-packed, or pouched with custom branding and labels for private label clients.
- Packaging includes tamper-evident seals and meets regulatory labeling requirements.
- Final Release and Shipping:
- A final round of testing ensures the batch meets all specifications.
- Products are shipped to clients or distributors, with documentation for traceability.
Choose the Right Package for Your Softgel capsule
Choosing the right packaging for your softgel capsules is critical to ensure product integrity, consumer appeal, regulatory compliance, and brand alignment. The packaging must protect the softgels from environmental factors (e.g., moisture, light, oxygen), enhance shelf life, and meet market demands for convenience and sustainability. Below are key considerations and options for selecting the most suitable packaging for your softgel capsules, tailored to the context of softgel contract manufacturing.

- Plastic Bottles:
- Description: HDPE or PET bottles with screw caps, often with desiccant packets to control moisture.
- Pros:
- Durable, lightweight, and cost-effective.
- Resealable for daily use; available in various sizes (e.g., 30, 60, 120 counts).
- Tamper-evident and child-resistant options.
- Cons:
- Less eco-friendly unless recyclable materials are used.
- Bulkier for travel compared to blisters.
- Best For: High-volume supplements like fish oil or multivitamins, where consumers need long-term supply.
- Blister Packs:
- Description: Individual softgels sealed in plastic or foil-backed cavities, often in carded sheets.
- Pros:
- Excellent protection against moisture, light, and air.
- Portable, single-dose convenience for on-the-go use.
- Tamper-evident and precise dosing.
- Cons:
- Higher per-unit cost for small runs.
- Less eco-friendly unless using recyclable materials.
- Best For: Premium or single-dose products, travel-friendly supplements, or clinical trial samples.
- Pouches:
- Description: Flexible, resealable foil or plastic pouches, often with zip-lock features.
- Pros:
- Lightweight, compact, and cost-effective for shipping.
- Customizable for branding with vibrant graphics.
- Good barrier properties with multi-layer materials.
- Cons:
- Less rigid, offering less physical protection than bottles.
- May not suit high-volume products.
- Best For: Boutique or eco-conscious brands, smaller batch sizes, or subscription models.
- Glass Bottles:
- Description: Amber or clear glass bottles with screw caps, often used for premium products.
- Pros:
- Premium aesthetic, appealing to high-end markets.
- Recyclable and reusable, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Excellent barrier against moisture and light (especially amber glass).
- Cons:
- Higher cost and weight, increasing shipping expenses.
- Fragile, requiring careful handling.
- Best For: Luxury supplements (e.g., high-potency CBD, specialty nutraceuticals).
- Sachets or Stick Packs:
- Description: Single-dose foil or plastic packets for one or a few softgels.
- Pros:
- Highly portable and convenient for single servings.
- Strong barrier properties for shelf stability.
- Ideal for sampling or promotional distribution.
- Cons:
- Higher packaging cost per dose.
- Generates more waste for frequent use.
- Best For: Trial packs, travel kits, or premium single-dose products.
- Plastic Bottles:
What Makes Us Unique As A Softgel capsule manufacturer?
As a softgel capsule manufacturer, several unique features can set your operation apart in the competitive nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and dietary supplement markets. Based on industry insights and practices from leading manufacturers, here are the key factors that can make a softgel capsule manufacturer stand out, tailored to highlight distinctive capabilities.
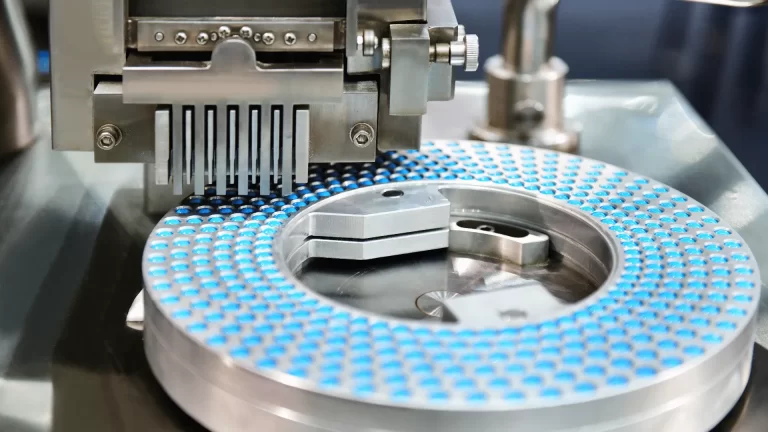
- Specialized Expertise in Liquid & Semi-Solid Fills: Softgel manufacturing is uniquely suited for oils, liquids, and suspensions. A key differentiator is a manufacturer's deep expertise in formulating, blending, and accurately encapsulating these specific types of fills, especially for challenging ingredients.
- Advanced Encapsulation Technology: Softgel production requires highly specialized rotary die encapsulation machinery. Uniqueness can stem from having state-of-the-art equipment, high production capacity for softgels, and the technical skill to run these complex machines efficiently and precisely.
- Mastery of Shell Formulations (Including Vegetarian): While gelatin is traditional, expertise in developing and manufacturing Vegetarian/Vegan softgel shells (using ingredients like modified starches or carrageenan) is a significant differentiator for manufacturers catering to specific dietary markets. Knowledge of how different fills interact with various shell materials is crucial.
- Ability to Produce Diverse Shapes and Sizes: Beyond standard ovals and oblongs, a manufacturer's capability to produce a wide variety of softgel shapes (rounds, tubes, chewables, twist-offs, novel shapes) and a broad range of fill volumes allows brands greater product differentiation.
- Proficiency in Functional Softgel Technologies: Offering specialized softgel types like enteric-coated, chewable, or delayed-release softgels (developed through shell modifications or specialized coatings) demonstrates advanced technical capability and allows brands to meet specific consumer needs or improve ingredient delivery.
- Rigorous Softgel-Specific Quality Control: Ensuring the quality of softgels requires specific testing beyond hard capsules, such as verifying the integrity of the hermetic seal, testing for leaks, assessing shell elasticity and firmness, and ensuring accurate liquid fill volume. A manufacturer's robust QC program tailored to softgels is a key USP.
- Stability Expertise for Liquid Formulations: Liquid and semi-solid fills can present unique stability challenges (e.g., oxidation). Expertise in formulating stable fills and using packaging solutions that protect against degradation (like a good softgel seal and appropriate bottling/blistering) is vital.
- Comprehensive Turnkey Services for Softgels: While many manufacturers offer turnkey solutions, one specializing in softgels can uniquely integrate softgel-specific formulation, stability testing, and packaging solutions seamlessly into their full-service offering.
softgel contract manufacturing Certification
We at softgel contract manufacturer to the following standards and requirements.






Frequently Asked Questions About capsule supplement manufacturing
A softgel is a solid dosage form consisting of a one-piece, hermetically sealed soft shell that encapsulates a liquid, semi-solid, or suspension fill. The shell is typically made from gelatin or vegetarian alternatives, along with water and a plasticizer.
Softgels are particularly well-suited for encapsulating oils and liquid-based ingredients, which may have better bioavailability or stability in this form. They are often easier to swallow than tablets and can effectively mask unpleasant tastes or odors. The sealed nature also protects sensitive ingredients from oxidation and degradation.
Ingredients that are liquid at room temperature, dissolved in an oil or liquid base, or stable suspensions/pastes are ideal for softgels. This commonly includes fatty acids (like Omega-3 fish oil), fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), CoQ10, plant oils, and certain herbal extracts.
Yes, for many fat-soluble or poorly soluble nutrients, encapsulating them in a lipid (oil) base within a softgel can enhance their absorption and bioavailability compared to powder or tablet forms.
Traditional softgel shells are made primarily from animal gelatin (often bovine or porcine), purified water, and a plasticizer like glycerin or sorbitol, which gives the shell its flexibility.
Many manufacturers now offer vegetarian and vegan softgel shells made from plant-based materials such as modified starches, carrageenan derived from seaweed, or HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose).
The primary difference is the source material (animal vs. plant). Vegetarian options cater to dietary restrictions. There can also be subtle differences in dissolution properties, moisture content, and compatibility with certain fill formulations, though modern vegetarian softgels are designed to perform comparably to gelatin.
Yes, softgels are specifically designed for these types of fills. Manufacturers are equipped to handle a wide range of viscosities and formulations, including solutions, suspensions, and pastes.
Materials that are highly aqueous (water-based) or have very low pH can be problematic as they can degrade the softgel shell over time. Dry powders are generally not encapsulated in softgels; hard capsules are more suitable for powders.
The sealed softgel shell is very effective at masking unpleasant odors and tastes. This is one of the key advantages of this dosage form, particularly for ingredients like fish oil or garlic.
Softgels come in many shapes, with Oval, Oblong, and Round being the most common. Other shapes include Tube, Suppository, and various novelty shapes (like fish). Sizes are designated by their approximate fill volume.
Softgel size is typically measured by the approximate volume of the fill material, commonly expressed in Minims or Cubic Centimeters (CC or mL). (Note: 1 CC is approximately 16.23 Minims).
Yes, manufacturers often offer customization options for color (using approved colorants), opacity, and printing (with food-grade ink). Custom shapes or specific non-standard sizes may be possible depending on the manufacturer's tooling capabilities, but usually involve higher MOQs.
Softgels are typically made using the rotary die encapsulation process. This involves simultaneously creating two ribbons of gel shell material, accurately injecting the liquid or semi-solid fill between them, and then cutting and sealing the softgels in one continuous operation. The softgels then go through a drying process.
Precise metering pumps are used during encapsulation to ensure the correct volume of fill material is injected into each softgel. In-process checks, including monitoring fill volume and weight variation, are performed frequently during the production run.
Quality control includes testing raw materials, in-process checks (like shell thickness, fill volume, seal integrity), and testing of the finished product. Finished softgels are visually inspected, and tested for parameters like fill weight/volume, disintegration/dissolution, and microbial limits.
Testing methods include visual inspection, physical tests to check the strength of the seam, and sometimes placing softgels under vacuum or pressure in a liquid medium to observe for leaks.
Finished product testing typically includes assay testing to confirm the potency (amount of active ingredient), purity testing for contaminants (like heavy metals or residual solvents), and microbial testing to ensure safety. Stability testing is also performed to determine the shelf life.
Yes, enteric coating can be applied to softgels. This coating prevents the softgel from dissolving in the acidic stomach, allowing it to pass into the small intestine before releasing its contents. Benefits include protecting ingredients from stomach acid, preventing stomach irritation, and reducing issues like "fish burps."
Yes, some manufacturers produce chewable softgels with modified shells and often flavored fills. They are a good option for consumers who have difficulty swallowing pills, such as children or the elderly, and provide a more pleasant consumption experience.
Yes, twist-off softgels are a type designed with a tab that can be twisted or snipped off to dispense the liquid fill. They are useful for precise dosing of liquids, particularly for infants, pets, or for products intended for topical application.

