
L-Asparaginase
Choose Gensei as your reliable L-Asparaginase supplier for a consistent source of this vital enzyme. L-Asparaginase plays a critical role in specific medical treatments due to its unique l asparaginase mechanism of action, targeting the metabolism of L-asparagine. While the term l asparagine supplement might appear in searches, it’s crucial to differentiate between the enzyme and the amino acid substrate.
As a reputable L-Asparaginase supplier, we understand the importance of safety and efficacy. Therefore, we provide detailed information regarding the l asparaginase side effect profile and ensure our product adheres to strict quality control measures. The intricate l asparaginase structure is key to its function, and we maintain conditions that preserve its activity.
Understanding potential l asparaginase toxicity is paramount in its application. While l asparagine powder refers to the amino acid itself, our focus is on the enzyme that acts upon it. The l asparagine solubility of the substrate is a separate characteristic from the enzyme’s properties. Trust Gensei as your L-Asparaginase supplier for a high-quality product backed by comprehensive technical support.
Please note: We are a wholesale supplier and have minimum order quantities.
Have questions about this product? Our team is here to help. For inquiries about multiple ingredients, please use the Contact Us option and include the list of ingredients in your message.
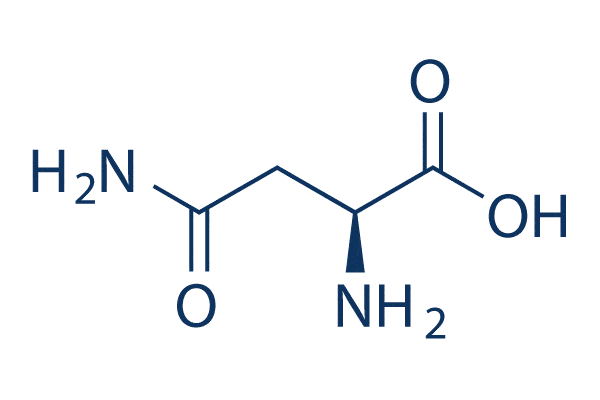
L-Asparagine CAS No.: 70-47-3
Chemical Name: (S)-2-Amino-3-carbamoylpropanoic acid
Synonyms:
- (S)-Asparagine
- L-α-Asparagine
- Asn
- (S)-2-Aminosuccinamic acid
- L-Asparagine monohydrate (often commercially available as this)
CB Number: CB1968872
Molecular Formula: C₄H<0xE2><0x82><0x88>N₂O₃ (Anhydrous) / C₄H<0xE2><0x82><0x88>N₂O₃ · H₂O (Monohydrate)
Molecular Weight: 132.12 g/mol (Anhydrous) / 150.13 g/mol (Monohydrate)
MDL Number: MFCD00006421
L-Asparaginase Manufacturing Process Flowchart
L-Asparaginase is typically produced through microbial fermentation. This flowchart outlines the general process.
(e.g., *E. coli*, *Erwinia chrysanthemi*)
(Culturing Microorganisms in a Nutrient-Rich Medium
to Produce L-Asparaginase)
(Separation of Microbial Cells from the Fermentation Broth
via Centrifugation or Filtration)
(Breaking Open the Microbial Cells to Release Intracellular L-Asparaginase)
(Separation of L-Asparaginase from Cellular Debris)
(Removal of Other Proteins, Nucleic Acids, and Contaminants
using Techniques like Chromatography, Ultrafiltration)
(Increasing the Concentration of the Purified L-Asparaginase Solution)
(Preparing the Enzyme in a Suitable Form for Storage and Use,
e.g., Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying) into a Powder)
(Testing for Enzyme Activity, Purity, Sterility,
Endotoxin Levels, etc.)
(Aseptic Packaging and Storage Under Controlled Conditions)
This flowchart provides a general overview of the L-Asparaginase manufacturing process through microbial fermentation. Specific steps and methods may vary depending on the microorganism used and the desired product specifications.
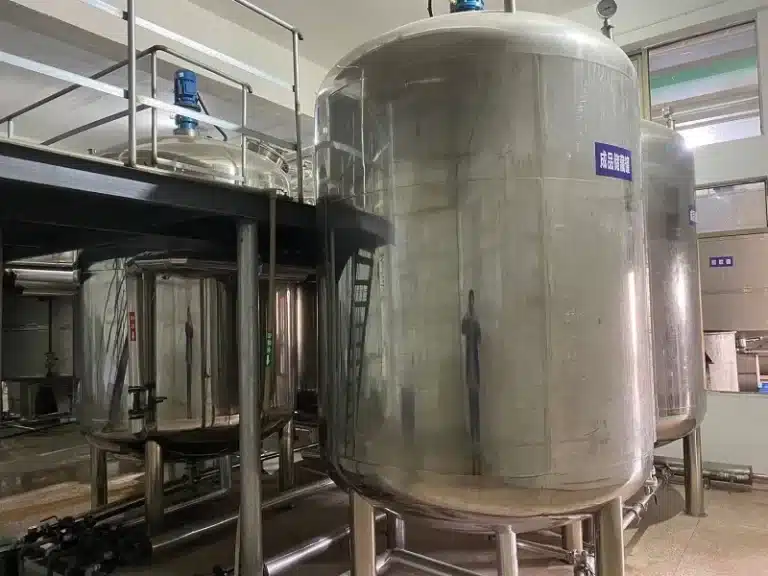
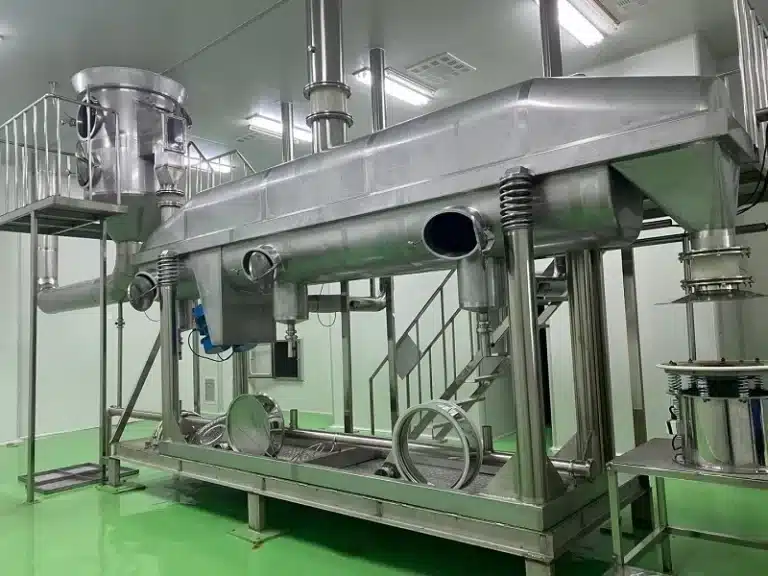
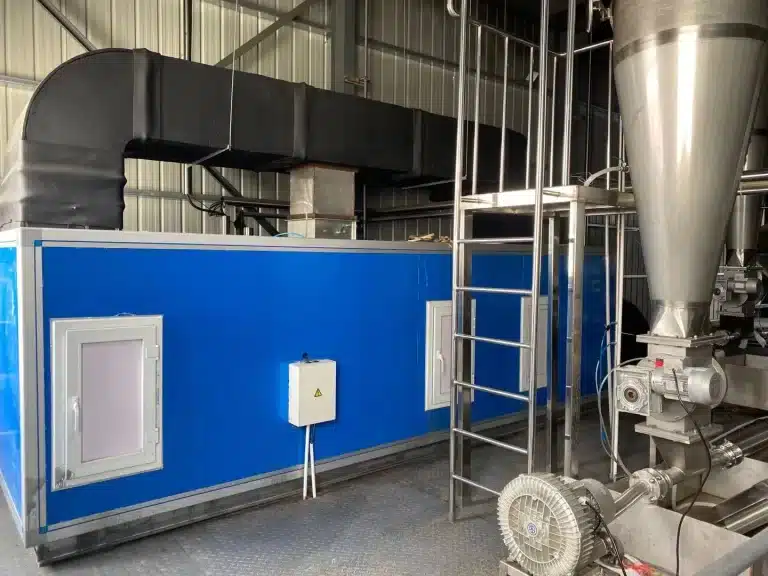
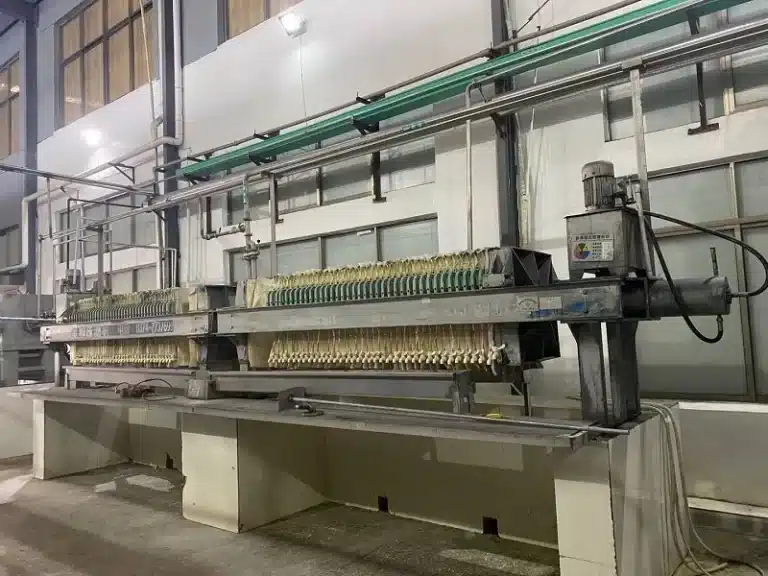
Our State-of-the-Art Manufacturing Facilities
Explore our modern facilities equipped with advanced technology to ensure the highest quality in the production of your vitamins, herbal extracts, minerals, and amino acids.











FAQs
L-Asparagine is a non-essential amino acid, meaning the human body can synthesize it. It plays a role in various metabolic processes, including the synthesis of proteins and other amino acids.
L-Asparagine is found in various plant and animal sources, including asparagus (from which it gets its name), soybeans, eggs, dairy products, and seafood.
It is primarily used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It also plays a role in the urea cycle and can be converted to aspartic acid.
No, L-Asparagine is considered a non-essential amino acid for humans.
Asparagine has an amide group (-CONH₂) on its side chain, while aspartic acid has a carboxylic acid group (-COOH).
Certain cancer cells, particularly some types of leukemia, have a high dependence on external sources of L-Asparagine for growth. The enzyme L-Asparaginase is used in chemotherapy to deplete the levels of L-Asparagine in the blood, thereby inhibiting the growth of these cancer cells.
While not as common as some other amino acid supplements, L-Asparagine is available as a dietary supplement. However, its use is not as widespread as other amino acids like glutamine or branched-chain amino acids.
Information on the side effects of L-Asparagine supplementation in healthy individuals is limited. As with any supplement, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before taking it.
L-Asparagine is generally poorly soluble in water compared to some other amino acids. Its solubility can be affected by temperature and pH.
Aspartame is an artificial sweetener composed of two amino acids: aspartic acid and phenylalanine. Asparagine is a different amino acid.
- Allergic Reactions: These are quite common and can range from mild skin rashes and hives to severe anaphylaxis (difficulty breathing, swelling, low blood pressure). Anaphylaxis is a serious and potentially life-threatening reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and diarrhea are frequent.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Feeling unusually tired or weak is a common complaint.
- Fever and Chills: Some patients may experience fever and chills during treatment.
- Headache: Headaches can occur.
- Injection Site Reactions: Pain, swelling, redness, or itching at the injection site (if administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly).
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, which can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Liver Problems: L-Asparaginase can affect liver function, leading to elevated liver enzymes, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and in rare cases, liver failure.
- Blood Clots (Thrombosis): Increased risk of blood clots in veins or arteries.
- Bleeding Problems: Paradoxically, while blood clots are a risk, some patients may experience bleeding issues.
- Kidney Problems: Although less common than liver issues, kidney problems can occur.
- Neurological Problems: These can include confusion, drowsiness, seizures, and rarely, coma.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Beyond typical allergic reactions, some patients may develop more severe hypersensitivity syndromes.
- Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): L-Asparaginase can affect insulin production and lead to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Hypoalbuminemia (Low Albumin Levels): Albumin is a protein in the blood, and its levels can decrease during treatment.
- Increased Cholesterol and Triglycerides: Changes in lipid levels can occur.
- Monitoring: Patients receiving L-Asparaginase are closely monitored by healthcare professionals for the development of side effects. Regular blood tests are performed to check liver function, kidney function, blood sugar levels, and other parameters.
- Pre-medication: Often, patients receive medications like antihistamines, corticosteroids, or acetaminophen before L-Asparaginase administration to help prevent or reduce the severity of allergic reactions and other side effects.
- Reporting Side Effects: It is crucial for patients to report any new or worsening symptoms to their healthcare team immediately.
- Severe Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis): While common, a severe anaphylactic reaction is a sign of toxicity. This can involve difficulty breathing, throat swelling, a sudden drop in blood pressure, and loss of consciousness, requiring immediate medical intervention.
- Severe Liver Dysfunction: Markedly elevated liver enzymes, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and signs of liver failure indicate significant liver toxicity. This can impair the body's ability to metabolize drugs and produce essential proteins.
- Pancreatitis: Severe inflammation of the pancreas, characterized by intense abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and elevated pancreatic enzymes, is a serious toxic effect.
- Thromboembolism (Blood Clots): The formation of blood clots in major blood vessels (veins or arteries) is a serious toxicity that can lead to complications like pulmonary embolism or stroke.
- Bleeding Disorders: While less common, severe bleeding episodes can occur as a sign of L-Asparaginase toxicity affecting the body's coagulation system.
- Neurotoxicity: Severe neurological symptoms such as significant confusion, pronounced drowsiness, seizures, or even coma indicate neurotoxicity.
- Severe Kidney Dysfunction: A significant decline in kidney function, although less frequent than liver toxicity, can occur.
- Severe Hyperglycemia: Uncontrolled and very high blood sugar levels can be a sign of toxicity affecting insulin production.
- At 25°C (77°F), the solubility of L-Asparagine monohydrate in water is approximately 2.9 g per 100 mL of water.
- The solubility increases slightly with temperature. 1 For example, at 100°C (212°F), the solubility is around 10 g per 100 mL of water.

