Introduction
L-pyroglutamic acid, also known as 5-oxoproline, is a unique derivative of glutamic acid with distinctive biochemical properties and diverse applications in various fields. This comprehensive article aims to delve into the nature of L-pyroglutamic acid, its physical and chemical characteristics, natural sources, industrial and medical applications, potential health benefits, associated side effects, regulatory considerations, and future research directions.
What is L-pyroglutamic acid?
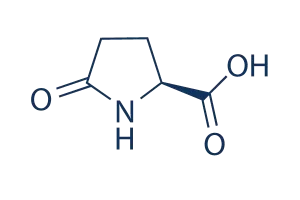
L-pyroglutamic acid is a non-proteinogenic amino acid derived from glutamic acid through cyclization involving the γ-carboxyl group. Structurally, it features a 5-membered lactam ring with a carboxyl group and an amino group attached to the same carbon atom. This molecular arrangement confers unique properties to L-Pyroglutamic acid, distinguishing it from other amino acids regarding its chemical reactivity and biological functions.
Physical and Chemical Properties
In its pure form, L-Pyroglutamic acid exists as a white crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water and ethanol due to its polar nature. The molecular formula of L-Pyroglutamic acid is C₅H₇NO₃, with a molecular weight of approximately 129.11 g/mol. It exhibits acidic properties with a pKa around 2.1 for the carboxyl group and a neutral pH in aqueous solutions.
Natural Sources of L-Pyroglutamic Acid
L-pyroglutamic acid is naturally present in certain foods and can also be synthesized endogenously in the body. Dietary sources include:
– Fruits (such as strawberries, peaches, and watermelon)
– Vegetables (spinach, cabbage)
– Dairy products (milk, cheese)
– Fermented foods (yogurt, kimchi)
The body also produces L-pyroglutamic acid as an intermediate in glutathione metabolism and other biochemical processes.
Synthesis and Production Methods
Commercial production of L-pyroglutamic acid involves chemical synthesis or microbial fermentation processes. Chemical synthesis typically starts from glutamic acid derivatives, which undergo cyclization under controlled conditions to yield L-Pyroglutamic acid. Microbial fermentation using specific strains of bacteria or fungi offers an alternative, more environmentally friendly approach to producing L-Pyroglutamic acid.
Applications in Different Fields
Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications
L-pyroglutamic acid is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations and medical treatments due to its role in metabolism and neuroprotection. It serves as a precursor for synthesizing glutathione, an essential antioxidant in detoxification and immune function. Glutathione supplementation, supported by L-Pyroglutamic acid, addresses oxidative stress-related conditions and supports overall cellular health.
Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements
L-pyroglutamic acid is incorporated into nutraceutical products and dietary supplements to promote cognitive function and mental clarity. It is believed to enhance neurotransmitter synthesis and improve memory retention and focus, making it popular among individuals seeking cognitive enhancement.
Cosmetics and Skincare
L-pyroglutamic acid is valued in cosmetic formulations for its moisturizing and skin-conditioning properties. It helps maintain skin hydration by acting as a humectant, attracting and retaining moisture in the epidermis. This makes it a common ingredient in moisturizers, serums, and anti-aging creams targeting dry or aging skin.
Industrial Uses
L-pyroglutamic acid finds applications in various industrial processes, including producing pharmaceutical intermediates, flavors, and fragrances. Its chemical versatility allows it to serve as a building block for synthesizing compounds with specific functional properties in industries ranging from food and beverage to fine chemicals.
Health Benefits of L-Pyroglutamic Acid
Cognitive Enhancement and Brain Health
L-pyroglutamic acid is believed to support cognitive function by enhancing neurotransmitter activity in the brain. It synthesizes glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter involved in learning, memory, and cognitive processes. Supplementation with L-pyroglutamic acid is purported to improve mental clarity, focus, and overall cognitive performance.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties
L-pyroglutamic acid contributes to antioxidant defenses within cells as a precursor for glutathione synthesis. Glutathione is a potent scavenger of free radicals and reactive oxygen species, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage associated with aging, inflammation, and chronic diseases.
Skin Hydration and Anti-aging Effects
In skincare products, L-pyroglutamic acid functions as a humectant, drawing moisture into the skin and maintaining hydration. Adequate hydration helps plump the skin, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and promote a youthful complexion. Regularly using L-Pyroglutamic acid-containing skincare products may improve skin texture and overall radiance.
Detoxification Support
Glutathione, synthesized from L-Pyroglutamic acid, plays a crucial role in detoxifying harmful substances in the body, including heavy metals and environmental toxins. Enhanced glutathione levels support liver function and facilitate the removal of toxins, promoting overall detoxification and metabolic health.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While L-pyroglutamic acid is generally considered safe when used as directed, excessive intake or individual sensitivity may lead to potential side effects. These can include:
– Gastrointestinal disturbances (such as nausea or diarrhea)
– Allergic reactions in sensitive individuals
– Interactions with medications affecting neurotransmitter levels or glutathione metabolism
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions or allergies should consult healthcare professionals before using products containing L-Pyroglutamic acid to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Regulatory Aspects and Safety
Depending on its intended use, L-pyroglutamic acid is regulated as a dietary supplement or food additive in various countries. Regulatory authorities, such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States, establish guidelines to ensure the safety, quality, and appropriate labeling of products containing L-pyroglutamic acid.
Future Directions and Research
Ongoing research endeavors continue to explore new therapeutic applications and biochemical roles of L-pyroglutamic acid. Advances in biotechnology and pharmaceutical sciences may lead to innovative uses in neuroprotection, skin health, and metabolic disorders. Further elucidation of its mechanisms of action and interactions with cellular processes holds promise for expanding its applications and enhancing human health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, L-Pyroglutamic acid emerges as a multifaceted compound with diverse health, nutrition, and industrial chemistry applications. From its foundational role in neurotransmitter synthesis to its contributions to antioxidant defenses and skin hydration, L-Pyroglutamic acid exemplifies the biochemical versatility of amino acids in supporting human health and technological advancement. As scientific understanding advances, continued exploration of L-Pyroglutamic acid promises to uncover new therapeutic potentials and expand its utility across various fields, underscoring its significance in contemporary science and industry.
We gain valuable insights into how biochemical compounds contribute to human well-being and scientific innovation through a comprehensive exploration of L-Pyroglutamic acid—from its molecular structure to its practical applications. Embracing the potential of L-pyroglutamic acid reinforces its role as a cornerstone in advancing health, nutrition, and industrial processes on a global scale.