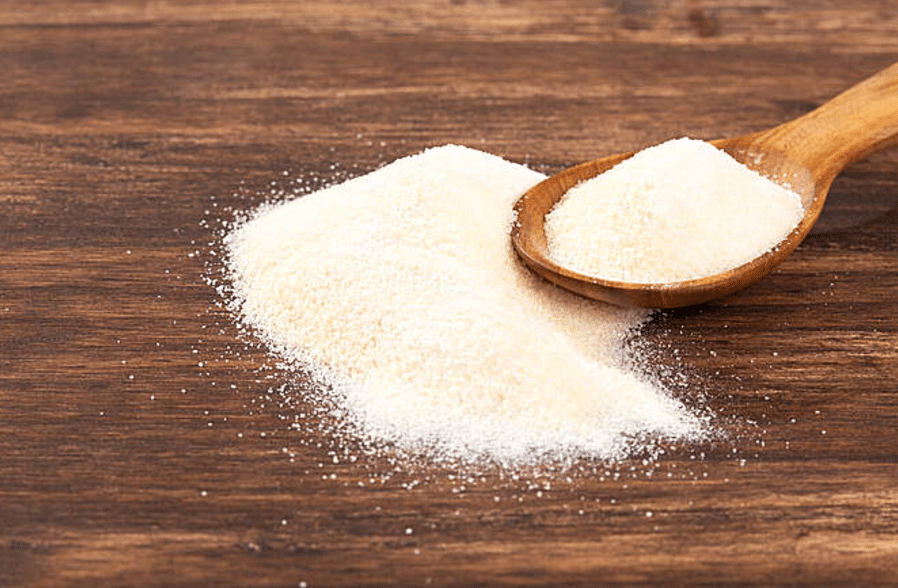

Gelatin Manufacturer
Seeking a reliable gelatin supplier? Gensei is a reputable gelatin factory, offering premium gelatin products with various gel strengths. We provide gelatin wholesale and gelatin bulk options, ensuring our gelatin meets the highest quality standards. Our gelatin is suitable for a wide array of applications, from food to pharmaceuticals to industrial uses. Choose Gensei for excellent quality, reliable supply, and competitive pricing from a leading gelatin factory manufacturer.
Please note: We are a wholesale supplier and have minimum order quantities.
Have questions about this product? Our team is here to help. For inquiries about multiple ingredients, please use the Contact Us option and include the list of ingredients in your message.
Gelatin CAS No.: 9000-70-8
Chemical Name: Gelatins, hydrolyzates
Synonyms:
- Edible Gelatin
- Hydrolyzed Collagen (sometimes used interchangeably, though gelatin is partially hydrolyzed collagen)
CB Number: CB4852570
Molecular Formula: Not applicable, as gelatin is a complex mixture of proteins.
Molecular Weight: Not applicable, as gelatin is a mixture of protein molecules with a wide range of molecular weights, typically from 10,000 to 100,000 Daltons depending on the degree of hydrolysis.
MDL Number: MFCD00131675
gelatin manufacturing process
Gelatin is obtained by the partial hydrolysis of collagen extracted from animal raw materials.
Animal Collagen (e.g., Bovine Hides, Pig Skins, Bones)
Washing and cutting the raw material
Treating raw material with acid or alkali depending on the gelatin type (Type A or Type B) to prepare collagen for extraction
Extracting collagen using hot water
Removing impurities through filtration and other purification steps
Concentrating the collagen solution by evaporation
Ensuring microbial safety
Drying the purified solution to form gelatin
Grinding the dried gelatin into powder or granules of desired size
Packaging the gelatin product
This flowchart outlines the general process for gelatin manufacturing. Specific steps may vary depending on the manufacturer and type of gelatin produced.
Why Choose Gensei as Your Gelatin Supplier?
Choosing Gensei as your gelatin supplier means partnering with a reliable gelatin factory manufacturer. We specialize in producing high-quality gelatin with consistent gel strength and purity. Our gelatin factory is equipped with advanced technology to ensure top-tier production.
We offer gelatin wholesale and gelatin bulk supplies, providing flexible options for your business needs. As a dedicated gelatin supplier and gelatin factory manufacturer, Gensei is committed to reliable service and timely delivery. Choose Gensei for quality gelatin bulk you can trust.
Features and Benefits
- Source: Derived from collagen found in animal skin and bones.
- Gel Formation: Forms a thermo-reversible gel (gels when cooled, melts when heated).
- Solubility: Swells in cold water and dissolves in hot water.
- Protein Composition: A mixture of peptides and proteins.
- Versatile: Used as a gelling agent, thickener, stabilizer, or texturizer.
Applications
- Food Industry: Confectionery (gummies, marshmallows), desserts (jellies, mousses), dairy products, meat products.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Hard and soft capsules, tablet binders, suppositories, plasma expanders.
- Photography: Used as a binder for silver halide crystals in photographic film and paper.
- Industrial Uses: Adhesives, coatings, microencapsulation.
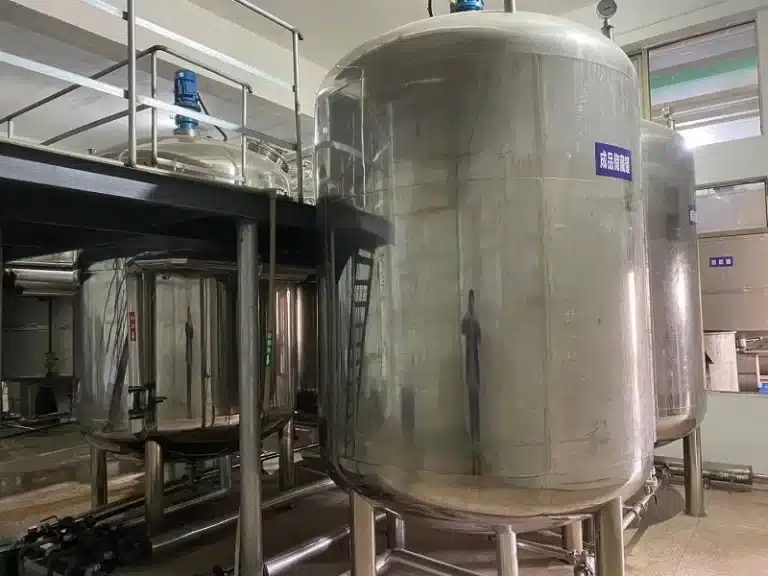
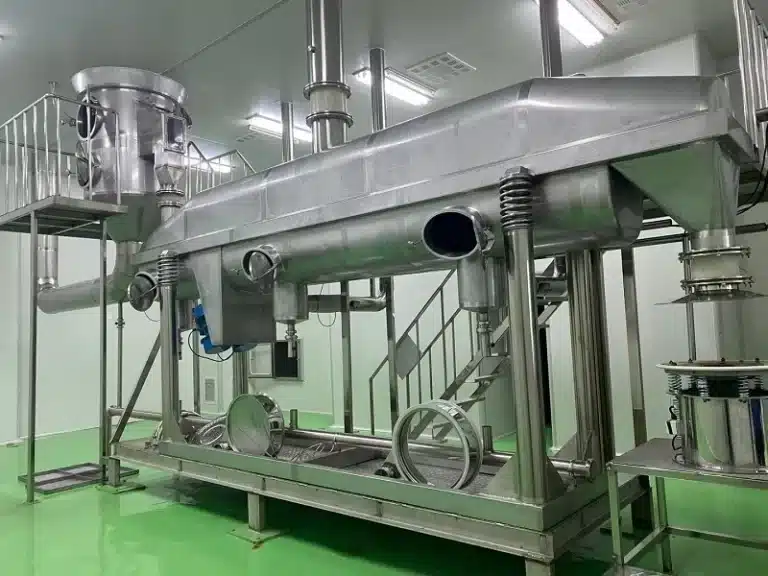
Our State-of-the-Art Manufacturing Facilities
Explore our modern facilities equipped with advanced technology to ensure the highest quality in the production of your vitamins, herbal extracts, minerals, and amino acids.











FAQs
Gelatin is a protein substance derived from collagen, which is found in animal tissues like skin and bones. It is obtained by the partial hydrolysis of collagen.
No, traditional gelatin is derived from animal collagen, so it is neither vegetarian nor vegan. Vegetarian and vegan alternatives exist, such as agar-agar, pectin, or carrageenan.
Gelatin is used as a gelling agent, thickener, stabilizer, and texturizer in foods (like desserts, gummies), pharmaceuticals (capsules, tablets), photography, and some industrial applications.
Gelatin is primarily protein, providing amino acids. However, it is not considered a complete protein because it lacks tryptophan and is low in other essential amino acids like lysine and methionine, so it should not be relied upon as a sole protein source.
Gelatin is made by processing animal raw materials containing collagen (like pig skins, cowhides, or bones) through pre-treatments (acid or alkali), extraction with hot water, purification, concentration, and drying.
Gelatin is generally considered safe for most people. In rare cases, it might cause mild digestive upset. Individuals with allergies to the source material (beef, pork) could potentially react.
Yes, gelatin forms a thermo-reversible gel. It will melt when heated and can re-gel when cooled again.
Bloom strength is a measure of the gel rigidity or gelling power of gelatin. A higher Bloom number indicates a stronger gel. It is a key quality parameter for gelatin.
Gelatin is primarily categorized into Type A (derived from acid-processed collagen, typically pig skin) and Type B (derived from alkali-processed collagen, typically bovine hides or bones). They differ slightly in properties like isoelectric point and gelling behavior.
No, gelatin is not the same as collagen. Gelatin is produced by partially hydrolyzing collagen. Collagen is a large, fibrous protein, while gelatin is a mixture of smaller protein peptides obtained from collagen.
While gelatin is derived from collagen (a component of joints and skin), consuming gelatin itself primarily provides amino acids. Collagen peptides (a more extensively hydrolyzed form of collagen) are generally considered more bioavailable and are specifically studied for joint and skin health benefits.

